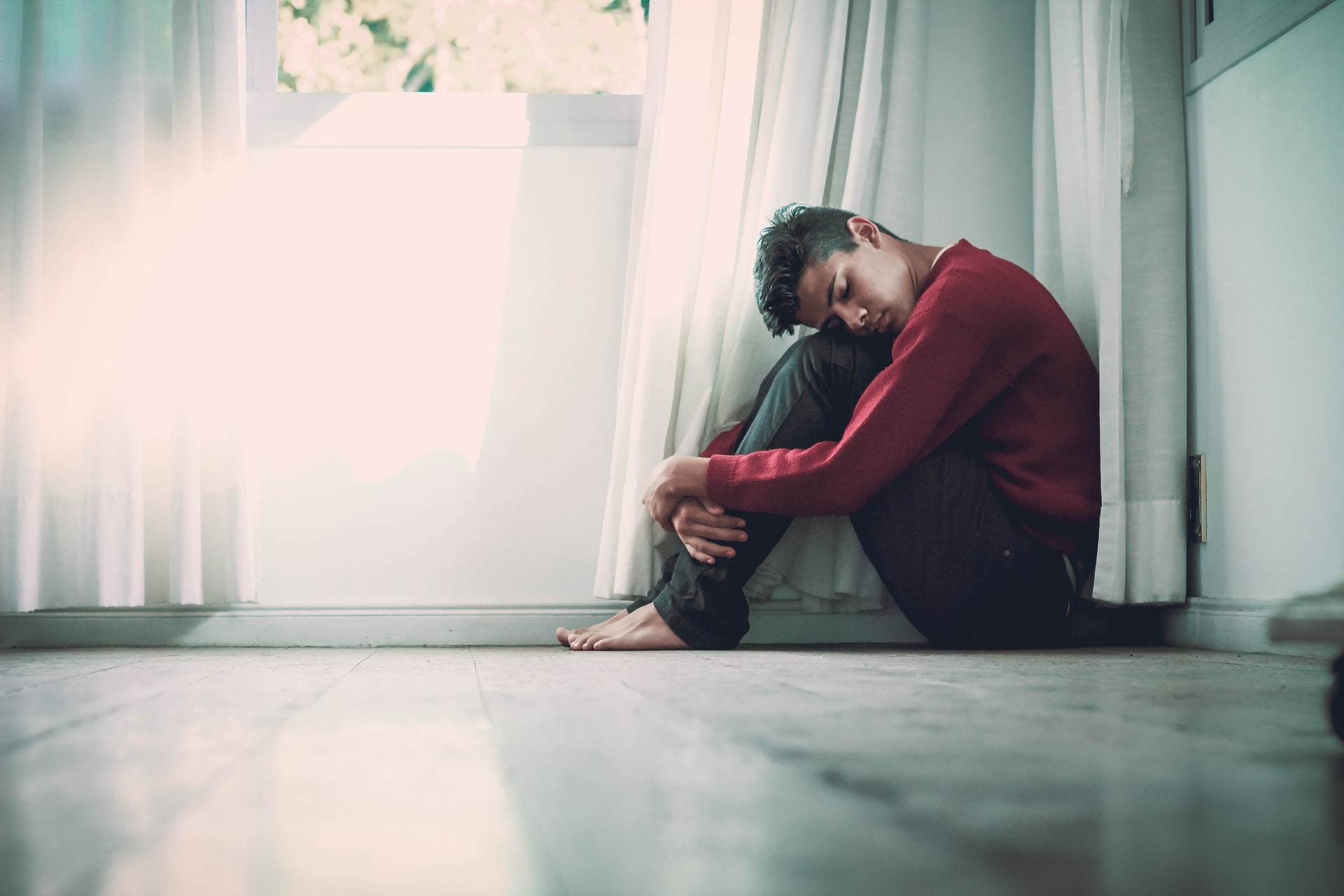
A study has recently been released that indicates that depression may be more closely related to an illness or allergic reaction than a mental condition.
Numerous scientists have spent the last several years studying the science behind what causes depression.
George Slavich, a clinical psychologist at the University of California, Los Angeles, has dedicated most of his career to the pursuit of understanding depression.
According to Slavich and other like-minded scientists, depression is not just a mental condition but affects the entire body like an illness.
“It does involve psychology, but it also involves equal parts of biology and physical health,” he said in an interview with The Guardian.
These scientists have found evidence that suggests that common signs of depression are similar to many of the common symptoms of general illness, such as chronic fatigue syndrome.
During a mild to moderate depressive episode, a person feels tired, restless, grumpy, has general aches and pains, and doesn’t feel like moving off the sofa. Many illnesses also have similar symptoms.
How is depression like an allergic reaction?
Furthermore, researchers have found that individuals with depression often suffer from chronic inflammation.
Inflammation is a healing response that alerts the body to activate the immune system and heal wounds. Proteins known as cytokines activate the immune system during times of illness.
However, research also indicates that both inflammation and cytokine levels increase dramatically when a person is suffering from a depressive episode.
Other inflammation-related diseases are also common in conjunction with depression. When cancer patients are given interferon alpha medication to boost the immune response (and thereby inflammation), a common side effect is often depression.
What causes inflammation?
Aside from traumatic events, wounds, and illness, chronic inflammation is also caused by a poor diet. A diet high in trans fats and sugar is linked to an increased chance for chronic inflammation.
Excess body fat also stores cytokines, triggering the immune response that leads to inflammation. Stress and loneliness are also known to lead to an increase in inflammation.
Because so many of the hallmarks of the modern lifestyle can cause excessive inflammation, some researchers have called depression an “allergy to modern life.”
Prevent inflammation and lower depression
The studies on depression as a side effect of inflammation and an unhealthy lifestyle are still in the early stages.
However, even though the link between depression and inflammation is not fully understood, it makes sense that improving quality of life would lower some risk factors.
According to a few clinical trials published in Molecular Psychology in 2006, when researchers added anti-inflammatory medicine to antidepressants, the symptoms of the depressed patients faded faster and increased the number of people who responded to treatment.
If you want to go the more natural route, curcumin and omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory effects.
Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and the avoidance of sugar, grains, and trans fats all work together to reduce total inflammation.
Combine these steps with regular social activity and you may find you have far fewer things to feel depressed about.